Chiho Kai
Mukogawa Women’s University, Japan
Title: A Cumulative Energy Deficit during 7 days is not a Predictor of Severity and Outcomes of Hospital – acquired Pressure Ulcer in Older Adult Patients
Biography
Biography: Chiho Kai
Abstract
Background: Pressure ulcer (PU) is a financial and physio-psychological burden in hospital settings, especially in the super-aged society.
Aim: To examine an association between energy deficit in the 7 days before PU development and the severity of hospital-acquired PU developed after admission in older adult patients.
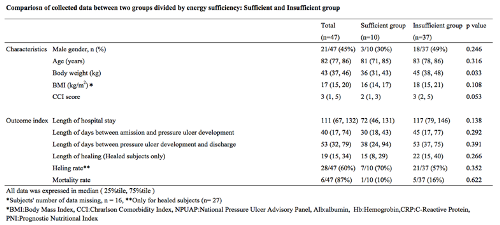
Methods: The study was conducted under a retrospective observational design in all consecutive patients admitted to a single general hospital between July 2014 and June 2016. Data collection: 1) demographics domain- sex, age, body weight, body mass index (BMI), Charlson comorbidity index (CCI), 2) PU domain- severity of PU scored by DESIGN-R score, NPUAP score, 3) blood test domain- hemoglobin (Hb), total lymphocyte count (TLC), serum albumin (Alb), C-reactive protein (CRP), Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI), 4) nutrition domain- cumulative and daily energy and protein intakes 7 days before and 7 or 14 days after PU development, 5) outcome domain- survival status, length of hospital stay in hospital, length of days between admission and PU development. Then the follows were compared: Method 1-blood test data on admission and at development of pressure ulcers; Method 2-all data for subjects between energy sufficient and deficit groups: Method 3- energy intake between mild (NPUAP stage I,II) and severe (stage III, IV).
Results: Method 1: Serum Hb level (p <0.001), serum Alb level (p <0.001), and PNI (p <0.001) at PU development were significantly lower than that on admission. Method 2: no parameters showed a significant difference in energy sufficient and deficit group. Method 3: no significant differences in energy intake during 7 days before PU development and time-related clinical outcomes between mild and severe PU. (Table)
Conclusion: The results of the present study suggests that nutrition support for energy sufficiency during the 7 days before PU development had no impact on the PU severity and time-related outcomes.